4 Key Differences Between Horizontal and Vertical Rescue Training

Introduction:
Rescue training isn’t a one-size-fits-all proposition. Depending on the environment and the challenges it presents, different skills, techniques, and equipment come into play. For the uninitiated, it might seem that rescue is rescue, no matter the setting. However, there’s a world of difference between horizontal and vertical rescue scenarios.
1. Nature of Risk Involved
Horizontal Rescue:
Ground Level Emergencies: Picture a scenario where an individual is trapped under debris after a building’s partial collapse. This situation demands quick thinking, spatial awareness, and precise communication. The risk here primarily revolves around ensuring safety while removing the debris without causing further harm.
Roadway Incidents: Imagine a vehicle accident with passengers trapped inside. The aim is to extract the passengers safely without aggravating their injuries. The terrain is flat, but the challenges are numerous.
Confined Space Rescues: Spaces such as underground tunnels or tanks present unique challenges. Restricted movement, limited visibility, and potential hazards like gases or chemicals make these rescues particularly tricky.
Vertical Rescue:
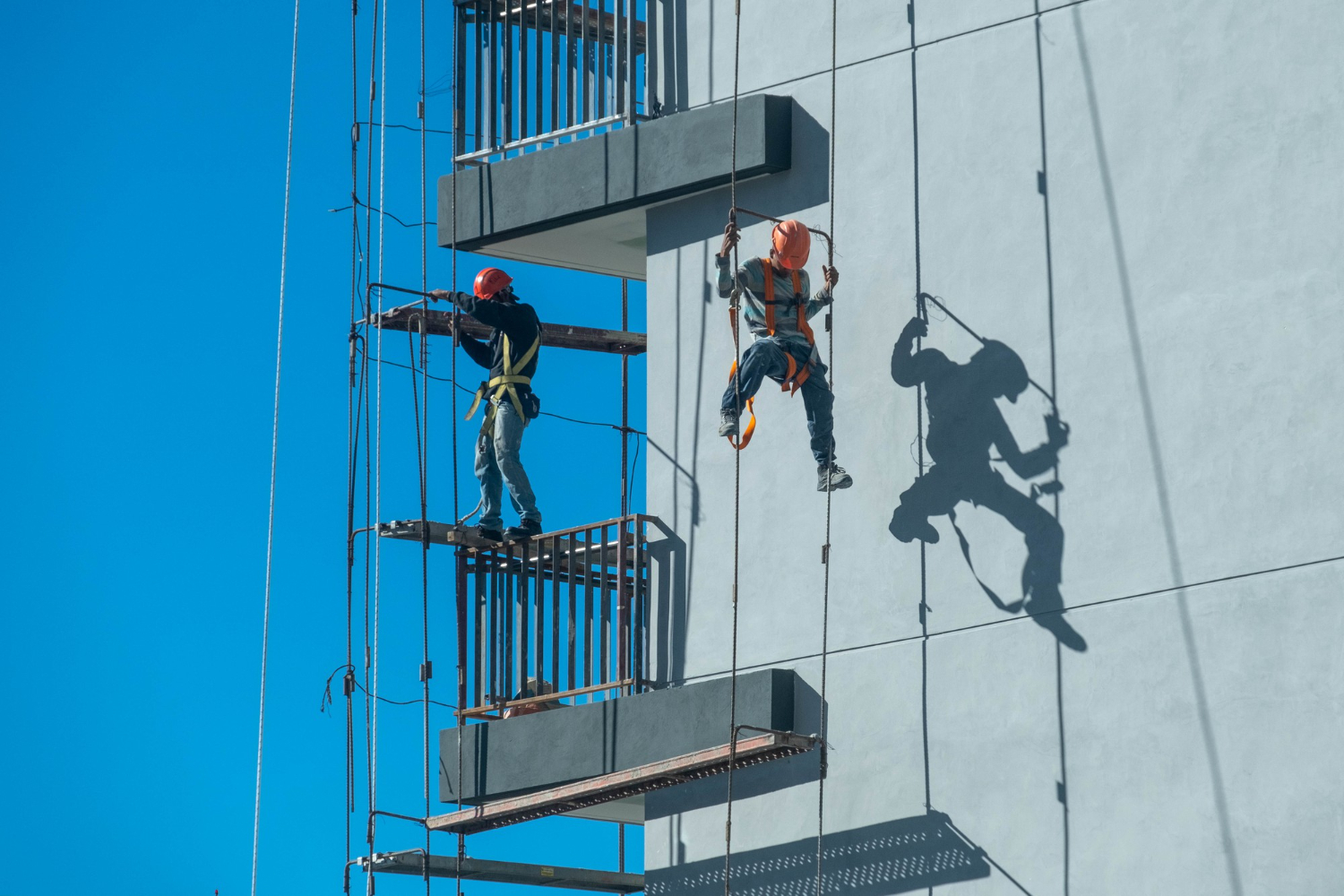
High-rise Incidents: One doesn’t need to look far to visualise a worker stranded on a high-rise building scaffold. The sheer height adds an immediate sense of gravity (quite literally) to the rescue.
Cliff Rescues: This involves saving someone stranded or injured halfway up a sheer cliff. Besides height, factors like loose rock or unpredictable weather add to the complexity.
Aerial Emergencies: Be it someone stuck on a malfunctioning ferris wheel or a worker on a malfunctioning crane, aerial rescues require utmost precision.
2. Equipment Used
Horizontal Rescue:
Ground Rescue Tools: Think of hydraulic tools that can cut or pry open metal. These are often required, especially in situations like vehicle extractions.
Extraction Devices: Devices specifically designed to safely pull individuals out of confined spaces or hazardous areas.
Stretchers: Used to carry the injured safely across a horizontal plane.
Vertical Rescue:
Ropes: Rope techniques are the backbone of vertical rescues. A reliable and robust rope can make the difference between life and death.
Pulley Systems: To hoist or lower rescuers and the rescued. Precision is key.
Harnesses: Safety is paramount, and a harness ensures that the rescuer remains safe while attending to someone.
Anchor Points: These are fixed points to which ropes are attached. They need to be incredibly secure to prevent any mishap.
3. Techniques Employed
Horizontal Rescue:
Entry and Extraction: It’s all about getting to the person in need safely and then ensuring a secure extraction.
Tunnelling: In confined space scenarios, rescuers sometimes need to tunnel their way to the person in distress.
Bracing: Essential when dealing with unstable structures. This technique ensures that the environment remains as safe as possible during the rescue.
Vertical Rescue:
Rappelling: A controlled descent down a rope, crucial in high places.
Hoisting: Pulling someone up, especially during cliff or high-rise rescues.
Anchor Establishment: Making sure your ropes have a secure point to hold onto. It’s the bedrock of any vertical rescue.
4. Training and Simulation Environments
Horizontal Rescue:
Mock Roadways: Training set-ups that mimic real-life road scenarios to prepare for vehicular accidents.
Simulated Confined Spaces: Replicas of tunnels or tanks to practice confined space rescues.
Flat Terrain Training: Areas designed to simulate ground-level emergencies.
Vertical Rescue:
Cliff Setups: Mock cliffs for training rescuers in mountainous or steep terrain emergencies.
Training Towers: Structures designed to mimic high-rise building scenarios, ensuring rescuers are well-practiced for the real deal.
High-rise Mock-ups: Simulating situations where workers or individuals are stranded on tall structures.
Conclusion:
In the vast realm of rescue operations, expertise in both horizontal and vertical scenarios is crucial. Rescuers need to be agile, adaptable, and thoroughly trained. Understanding the key differences is not just academic; it’s a matter of life and death. The challenges and risks involved in each type of rescue underscore the importance of thorough training and preparation.
We’d be remiss if we didn’t mention the significant role played by training institutions in preparing rescue personnel for these challenging scenarios. Vertical Horizonz, for instance, has carved a niche for itself in offering top-notch training for such situations. Nestled at 214 Leitchs Rd, Brendale QLD 4500, it’s a beacon for all those aspiring to be at the forefront of rescue missions, making a difference in critical times.
-
6 Career Advancements Enabled by Completing a White Card Training Course
November 06, 2023
-
7 Career Opportunities Unlocked by a Working at Heights Certification
October 24, 2023
-
7 High-Paying Jobs You Can Get with a GWO Training Certification
October 20, 2023
-
Top 7 Career Advancements After Completing a High Pressure Water Jetting Course
October 18, 2023
-
5 Essential Techniques Taught in High Pressure Water Jetting Courses
October 18, 2023
-
7 Career Opportunities after Completing Vacuum Loading Training
October 17, 2023